Transparent logistics processes
Logistics is more than simply storing goods and transporting them from A to B. Logistics is an important system performance that consists of several coordinated steps. Standards take on an important function as a link.
Logistics involves the use and control of information, financial and goods flows beyond one's own company. Planning, coordination and control of the value chain are the main tasks of logistics and enable effective handling of all processes involved. Transport is an important process within logistics and involves moving the required quantity of goods from the manufacturer to the consumer at the right time.
Logistics has developed into an important branch of the economy; thus, the demands on the industry have also grown in recent years. Customers are demanding ever shorter delivery times and the flow of goods has been increasing in volume for years. Digitalisation, environmental protection, cost efficiency and reliable delivery are further demands that the industry has to meet.
GS1 standards support the exchange of goods and services in logistics and reduce trade barriers along the logistics chain. As a common language worldwide, they ensure compatibility, transparency and cost efficiency. They include identification keys, standardised data carriers and communication standards.
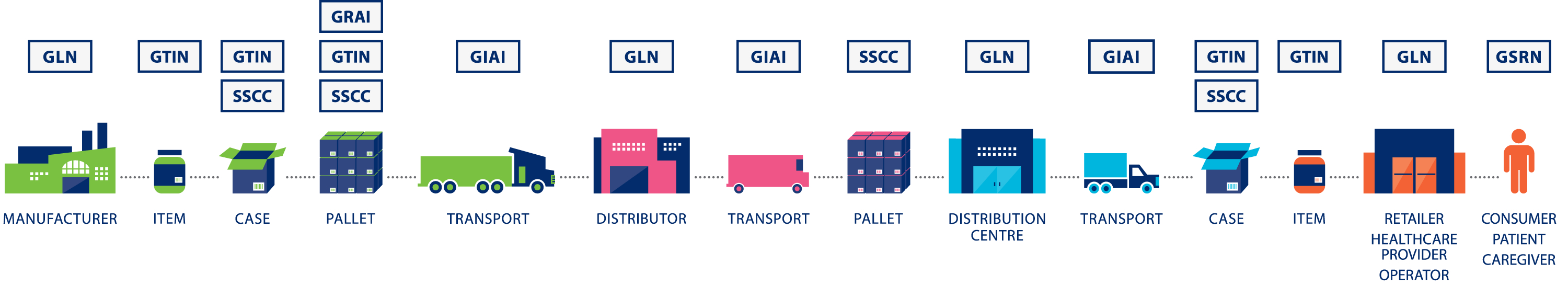
GS1 identification keys, including Global Trade Item Number (GTIN), Serial Shipping Container Code (SSCC) and Global Location Number (GLN), enable automatic data exchange and lead to interoperability between all stakeholders, creating an efficient, sustainable and collaborative logistics environment.
The Swiss logistics network:
Standards for logistics
For logistics industry, GS1 Switzerland offers a wide range of products and services that make all supply chain processes transparent and sustainably optimized.
Serial Shipping Container Code (SSCC)
The field of application of the SSCC are transport units, for example pallets, packages, shipping units and consignments of goods.
The harmonized parcel label supports the supply chain from the shipper to the customer by making the flow of goods recognizable for all parties in the supply chain with the unique identification of the shipment and does not require any manual intervention - such as relabeling repeated several times in the supply chain.
The GLN is used to identify locations and companies, for example a branch, unloading dock, external warehouse or billing address.
Global Returnable Asset Identifier (GRAI)
The GRAI is used for load carriers such as returnable containers, pallets, crates and beer kegs.
Global Identification Number for Consignment (GINC)
The field of application of the GINC are shipments, for example a logical grouping of different simultaneous shipments to the same destination.
Global Shipment Identification Number (GSIN)
The field of application of the GSIN are different deliveries, which are delivered together to one customer.
These topics might also interest you: